Research and development in Sweden 2021
Increased expenditures for R&D in Sweden
Statistical news from Statistics Sweden 2022-10-27 8.00
Expenditure on research and development (R&D) increased by 1.9 SEK billion in Sweden in 2021, despite continued challenges during the Covid-19 pandemic. All sectors contributed to the increase in R&D expenditure.
During 2021, intramural R&D expenditure amounted to 183 SEK billion in Sweden. This is an increase of 1.9 SEK billion, or 1 percent, compared to 2020 in fixed prices. Intramural R&D refers to research and development performed within organisations in Sweden.
- The total expenditure for intramural research and development increased during the pandemic, as opposed to previous economic crises, says Nils Adriansson, statistician at Statistics Sweden.
After the financial crisis in 2008, total R&D expenditure decreased by roughly 6 percent. In the Business enterprise sector, the decrease exceeded 10 percent between 2008 and 2009. However, in 2020 and 2021, the observed development has been to the contrary. Expenditures in R&D increased both in total and for the Business enterprise sector. The Government sector and the Higher education sector also increased their intramural R&D in 2021.
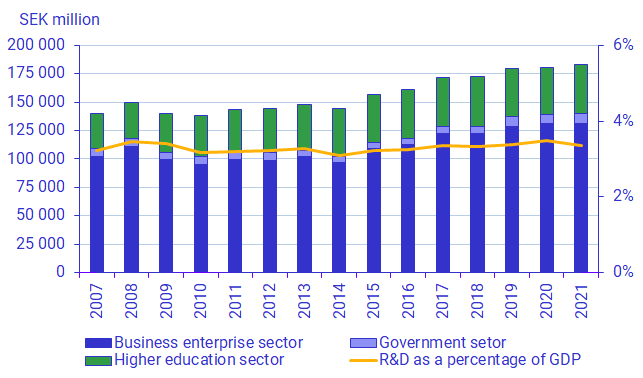
Although total expenditure on R&D increased in 2007–2021, the R&D intensity decreased. The R&D intensity is the total intramural R&D expenditure as a percentage of the gross domestic product (GDP). Both investments in R&D and the development of GDP thus affect R&D intensity. It was estimated at about 3.4 percent in 2021, a decrease by 0.1 percentage points since 2020. Hence, the R&D intensity 2021 was at approximately the same level as in 2019, before the pandemic.
Increased employees and less consultants
Personnel within R&D are categorised as either researchers or supporting staff. The majority are employees, i.e. internal personnel. External personnel consist of consultants and other types of leased personnel. In total, internal personnel amounted to almost 116,000 full-time equivalents. This is a small increase from 2020. A full-time equivalent corresponds to the work a full-time employee performs over a year.
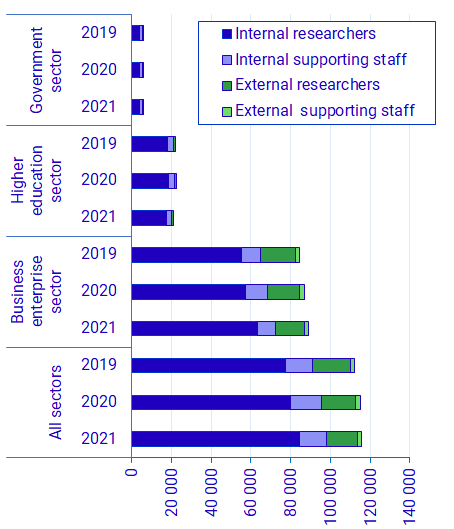
*External staff within the Higher education sector is assumed to consist only of researchers.
During the Covid-19 pandemic, the internal personnel has increased, while the external personnel has decreased. The same development can also be seen in the corresponding costs. A greater proportion of the total labour costs in 2021 were attributed to the internal personnel compared to 2019.
Different types of R&D in different sectors
Research and development can be categorised as basic research, applied research or experimental development. The diagram below shows how intramural R&D expenditure was distributed by type of R&D in the sectors in 2021.
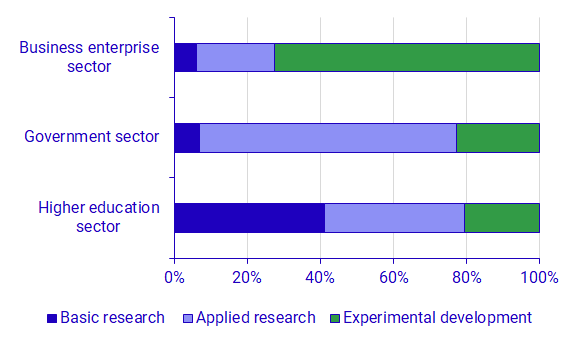
In the Business enterprise sector, experimental development is the most common type of R&D. Experimental development is systematic work, drawing on knowledge gained from research and practical experience and new ideas, aiming to produce new materials, products, services, systems, methods, or to improv those already existing.
In the Government sector, applied research is the most common type of R&D. Applied research is systematic work undertaken in order to acquire new knowledge or new ideas with a specific, practical aim or application. Thus, applied research tends to be more closely related to practical operations which could explain why this type of R&D is more common within the Government sector.
Basic research makes up a relatively large proportion of R&D in the Higher education sector. Unlike applied research, basic research does not have a specific intended application. Basic research is particularly common within natural sciences, humanities and the arts and social sciences.
Increased R&D investments in the Business enterprise sector
In 2021, intramural R&D expenditure in the Business enterprise sector amounted to 131.5 SEK billion, in fixed prices. This is an increase of 2.7 SEK billion, around 2 percent, compared to 2019.
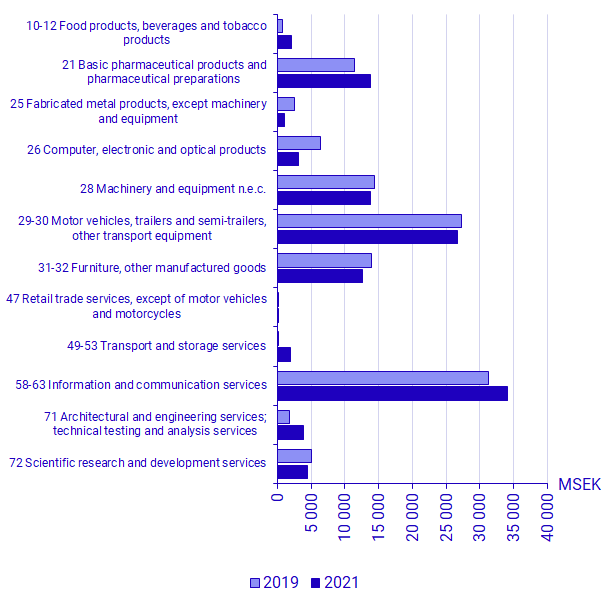
The product field information and communication services (SPIN 58–63) had the highest expenditure, 34 SEK billion. The group accounted for a quarter of the total R&D expenditure. The product group also had the largest increase between 2019 and 2021. Expenditure increased by 2.8 SEK billion, which means an increase of 9.1 percent. The product field basic pharmaceutical products and pharmaceutical equipment (SPIN 21) had the second largest increase with 2.4 SEK billion.
Increasing R&D funds to research on health in the Government sector
Total expenditure on intramural R&D in the Government sector amounted to 8.2 SEK billion in 2021. The regions were, as in previous years, the largest subsector with expenditures of approximately 4.6 SEK billion. This constitutes 56 percent of the total intramural R&D expenditure in the sector.
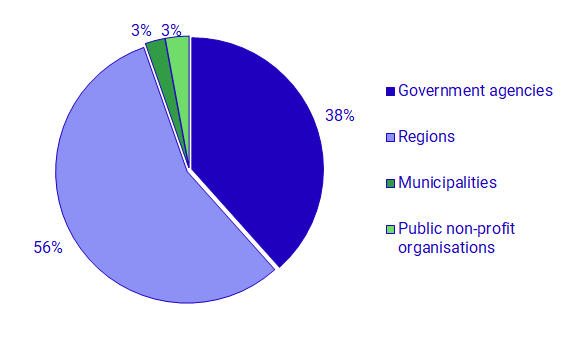
Government agencies’ R&D expenditure on health was about 216 SEK million. This is an increase by 37 percent compared to 2019. The regions, whose primary responsibility is health care services, also had increasing expenditure during 2021. Compared to 2019, the regions’ R&D expenditure on health care increased about 69 SEK million, or about 2 percent.
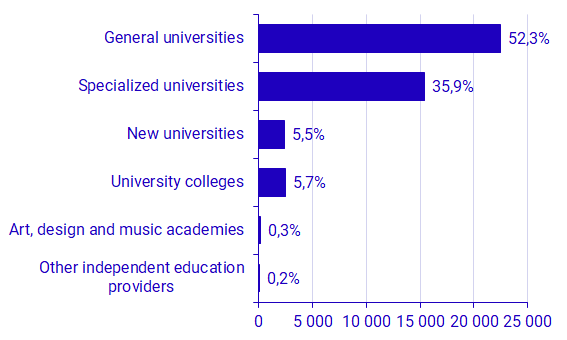
Six universities accounted for the majority of R&D expenditure
Total intramural R&D expenditure in the Higher education sector amounted to almost 43 SEK billion in 2021. Statistics show that there is a clear concentration of expenditure to a few universities. The majority of expenditure in 2021, about 52 percent, was attributed to the large general universities. This group consists of the universities of Uppsala, Lund, Gothenburg, Stockholm, Umeå and Linköping. These universities make up approximately 15 percent of the higher education institutions that perform R&D in Sweden. The six specialised universities accounted for about a third of the sector’s total expenditure, while the expenditure amongst the other higher education institutions amounted to about 12 percent.
A corresponding pattern also exists for R&D staff. Almost 85 percent of full-time equivalents in R&D were carried out at the large general universities and the specialised universities in 2021. The remaining higher education institutions make up around two-thirds of the total number of higher education institutions with R&D activities in Sweden. These institutions only account for around 15 percent of the R&D personnel resources within the sector.
Definitions and explanations
Research and Development (R&D)
Research and experimental development (R&D) comprise creative and systematic work undertaken in order to increase the stock of knowledge and to devise new applications of available knowledge in all fields of science.
To be defined as R&D, an activity must be:
Novel: An R&D activity undertaken in order to generate new knowledge and to devise new applications of available knowledge.
Creative:R&D activities based on original concepts or hypotheses.
Uncertain:The final outcome of R&D activities is generally uncertain. There is also uncertainty related to the cost or time needed to achieve the expected results.
Systematic:R&D activities are performed systematically and are planned and budgeted.
Transferable and/or reproducible:An R&D activity should lead to results that could possibly be transferable and/or reproducible.
Intramural R&D
Activities carried out in Sweden by the organisation’s own personnel or by consultants in an R&D project led by the organisation, in the organisation’s own R&D activities. Intramural R&D also includes R&D carried out by commission.
Extramural R&D
R&D activities that the organization has commissioned others to carry out as well as support for R&D that the company has provided to others, for example grants to universities and colleges.
Full-time equivalent in R&D
A full-time equivalent in R&D corresponds to the work a full-time employee performs over one year. A full-time employee who dedicates half their working time to R&D contributes with 0.5 full-time equivalents.
Basic research is experimental or theoretical work undertaken primarily to acquire new knowledge of the underlying foundations of phenomena and observable facts, without any particular application or use in view.
Applied research is original investigation undertaken in order to acquire new knowledge. It is, however, directed primarily towards a specific, practical aim or objective.
Experimental development is systematic work, drawing on knowledge gained from research and practical experience and producing additional knowledge, which is directed to producing new products or processes or to improving existing products or processes.
Private non-profit sector
Intramural R&D expenditures in the private non-profit sector are included in estimated totals. As the sector is relatively small in comparison to other sectors, the statistics are not reported separately. For statistics regarding the private non-profit sector see the Statistical database.
Fixed price calculation
Comparisons over time are presented in the 2021 price level to remove any price effects. For fixed price calculation, a GDP deflator is used.
GDP at market price in nominal and fixed prices is used and published at National-accounts.
R&D intensity is calculated as a percentage of the total intramural R&D expenditure as a share of real GDP.
SNI - Swedish Standard Industrial Classification
For more information, SNI.
The Quality of the statistics
Methodological changes have been implemented for the Higher education sector and the government sector, which affect comparability over time. Among other things, the Swedish Institute of Space Physics is now included in the reporting in the government sector. For further information on the production of the statistics, we refer to our documentation, Statistikens framställning (2021) and Kvalitetsdeklaration (2021). You can find these documents in Swedish at our product page. If you want help interpreting the results you are most welcome to contact us.
Next publishing will be
Every year in October, Statistics Sweden publishes statistics regarding R&D expenditure and personnel in Sweden. It is a part of Sweden's official statistics. More detailed analyses of the respective sectors will be published according to the dates below:
- 17th November, the Government sector
- 1st December, the Higher education sector
- 15th December, the Business enterprise sector
Statistical Database
More information is available in the Statistical Database
Feel free to use the facts from this statistical news but remember to state Source: Statistics Sweden.
