Research and development in the higher education sector, 2015:
A third of R&D FTE performed by doctoral candidates
Statistical news from Statistics Sweden 2016-12-16 9.30
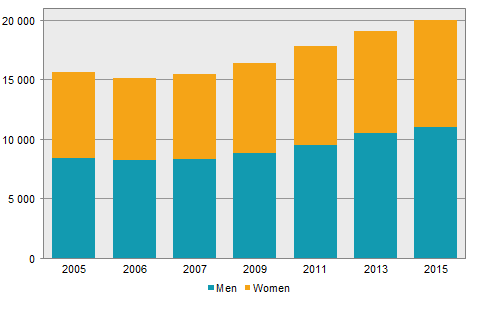
R&D expenditure in the higher education sector, including universities and other higher education institutions, continued the upward trend in 2015. In the higher education sector, the number of Full Time Equivalents (FTE) increased by 931 compared with 2013. Doctoral candidates performed a third of total FTE in R&D. Natural sciences and the R&D field of medical and health sciences are the largest fields of science and technology for R&D both in terms of revenue and expenditure.
In the higher education sector, the number of FTE amounted to 20 035 in 2015. Researchers’ R&D-related working time increased the most among the different employment categories. In 2015, they carried out 3 902 FTE, representing a 16 percent increase compared with 2013. Research engineers and laboratory assistants also increased the FTE in R&D. Doctoral candidates reduced their R&D FTE the most, by 370, or 5 percent. The largest decrease in percent was among post-doctoral fellows, where FTE dropped by 26 percent. The number of FTE carried out by non-employed personnel is estimated to be 1 400. As previously, men performed 55 percent of the total FTE in the higher education sector, while women accounted for 45 percent. Furthermore, men spent about 49 percent of their working time on R&D, while the corresponding figure for women was 44 percent.
Natural sciences and the R&D field of medical and health sciences are the largest fields of science and technology for R&D, both in terms of revenue and expenditure. Similarly, these two research areas have seen the largest increases in R&D expenditure between 2013 and 2015.
In constant 2015 prices, R&D expenditure in natural sciences increased by 10 percent, while the corresponding figure for medical and health sciences was 5 percent. Nevertheless, the largest increase in percentages was in agricultural and veterinary sciences, where R&D expenditure increased by 8 percent, after decreasing between 2011 and 2013. Personnel resources in R&D increased in particular among employees without a field of R&D; however, this increase could in part be due to an enhanced sample frame.
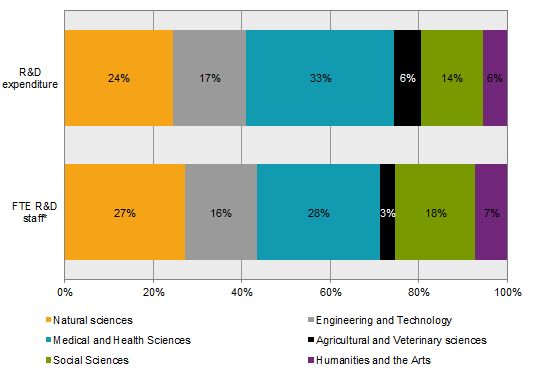
*Excluding FTE employed without an R&D field
Definitions and explanations
Research and Development (R&D)
Research is defined as systematic work to find new knowledge or ideas with or without the aim of a particular purpose. Development is defined as systematic work that uses research results, scientific knowledge or new ideas to bring about new material, goods, services, processes, systems, methods or significant improvements to those that already exist.
R&D expenditures
R&D expenditures include current expenditures and investments for intramural R&D. Current expenditures refer to labour costs, consultant fees, and other current expenditures. Investments include Buildings, land and real estate, Machinery and equipment, and Software.
FTE (Person-year)
A person-year is the work that one full-time employee does in one year. A full-time employee that uses half of their time for R&D in a year has therefore performed 0.5 R&D person-years.
Publication
Statistical Database
More information is available in the Statistical Database
Feel free to use the facts from this statistical news but remember to state Source: Statistics Sweden.
