Environmental Accounts – Emissions to air second quarter of 2018
Greenhouse gas emissions by the manufacturing industry increased in the second quarter of 2018
Statistical news from Statistics Sweden 2018-10-25 9.30
Greenhouse gas emissions by the Swedish economy increased by one percent in the second quarter of 2018 compared with the same quarter in 2017. This increase was mainly caused by higher emissions by the manufacturing industry. At the same time, emissions by the electricity, gas and heating industry decreased. The Swedish economy grew by three percent in the second quarter of 2018.
New quarterly statistics from the Environmental Accounts at Statistics Sweden measuring emissions from the Swedish economic actors and households are now available. In the second quarter of 2018, greenhouse gas emissions by the Swedish economy and households amounted to 15.5 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalents. This is 1.2 percent more than in the same quarter in 2017. In the same period, economic growth was 3.0 percent.
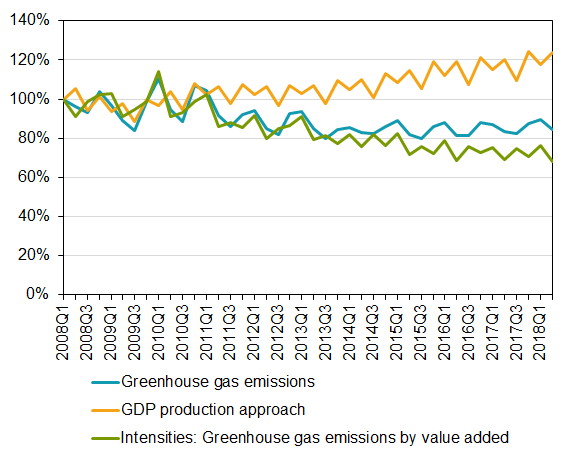
Source: Statistics Sweden, Environmental accounts and National accounts.
Greenhouse gas emissions by the manufacturing industry increased by 5.6 percent in the second quarter of 2017 compared with the same period in 2017. At the same time, value added in the manufacturing industry increased by 3.8 percent. The increase in emissions can be seen in manufacturing of coke and refined petroleum products, chemicals, pharmaceuticals products and manufacturing of basic metals.
Greenhouse gas emissions by the electricity, gas, heating, water and waste industries decreased by 4.7 percent in the second quarter of 2018 compared with the same quarter in 2017. Most greenhouse gas emissions come from electricity and heat production. Both emissions and value added in this industry vary seasonally and are often higher in the first and last quarter. The lower greenhouse gas emissions in the second quarter of 2018 are due to lower use of fossil fuels such as natural gas, peat and coal as a result of warm weather.
Greenhouse gas emissions in the construction and transport industries, as well as value added, have also increased compared with the same quarter in 2017. However, the estimated emissions in these industries should be interpreted with caution due to uncertainties in the model assessments.
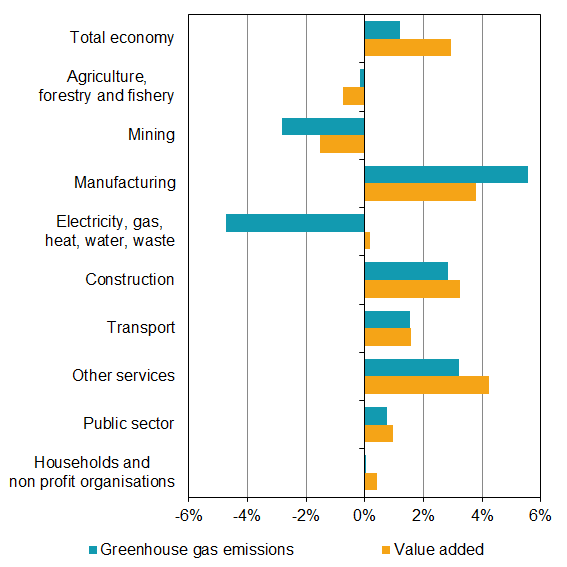
Source: Statistics Sweden, Environmental accounts and National accounts. Note: Only non-profit organisations, and not households, provide value added.
Developments in different industries
The connection between greenhouse gas emissions and industries’ contribution to the Swedish economy vary between industries. Some industries are emissions-intensive, and increased production means higher emissions, while other industries may increase value added without any significant increase in emissions levels.
| NACE 2007 industry | Greenhouse gas emissions | Value Added | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018Q2 | Change compared to same quarter 2017 | 2018Q2 | Change compared to same quarter 2017 | ||||
|
Agriculture, forestry and fishery
|
2 279 | ‑4 | ‑0.2% | 13 427 | ‑100 | ‑0.7% | |
|
Mining
|
447 | ‑13 | ‑2.8% | 4 910 | ‑76 | ‑1.5% | |
|
Manufacturing
|
3 573 | 188 | 5.6% | 161 954 | 5 929 | 3.8% | |
|
Electricity, gas, heat, water, waste
|
1 711 | ‑85 | ‑4.7% | 27 835 | 47 | 0.2% | |
|
Construction
|
495 | 14 | 2.8% | 76 958 | 2 420 | 3.2% | |
|
Transport
|
3 613 | 55 | 1.5% | 44 254 | 681 | 1.6% | |
|
Other services
|
844 | 26 | 3.2% | 517 465 | 21 015 | 4.2% | |
|
Public sector
|
171 | 1 | 0.8% | 212 970 | 2 002 | 0.9% | |
|
Households and non-profit institutions [1]
|
2 388 | 0 | 0.0% | 14 403 | 61 | 0.4% | |
|
Total economy
|
15 521 | 183 | 1.2% | 1 209 314 | 34 711 | 3.0% | |
1 Only non-profit organisations, and not households, provide value added.
Revisions
Since the previous publication on 2018-08-30, a number of revisions have been made:
- The model for emissions from mobile combustion is still based on the economic development in 2018 compared with 2017. This is because an important source, monthly fuel, gas and inventory statistics, uses a new approach from January 2018. All information concerning 2018 based on this source is preliminary and will be revised. All in all, this uncertainty affects mobile combustion, which accounts for 45 percent of greenhouse gas emissions and should be taken into account when reading the statistics. This uncertainty applies mainly to the development in 2018 in the transport sector, public sector, construction, other services, and households. The total increase in greenhouse gas emissions by mobile combustion is estimated at approximately one percent in the second quarter of 2018 compared with the same quarter of the previous year.
- Updated values on diesel led to minor changes compared with the last quarter, mainly in 2017Q3.
- Minor updates were made in the manufacturing industry and in the production of electricity gas and heating due to updates in Quarterly fuel statistics.
More information (in Swedish) on the revisions is available on the Environmental Accounts’ product page under Documentation.
Definitions and explanations
The Environmental Accounts are compiled within the framework of the System of Environmental and Economic Accounts (SEEA) and present national environmental statistics and economic statistics in the same framework, using NACE industry classification. Environmentally-related statistics connected to the system of national accounts enable an analysis of the Swedish economy and the impact that each industry has on the environment.
Emissions to air according to the environmental accounts is based on a production perspective and defined by the nationality of economic actors. Direct emissions from Swedish economic actors are included, regardless of where in the world emissions occur. This is called the residence principle and includes three parts:
- Emissions within the Swedish territory
- Deduct emissions by aviation, navigation and land transport from foreign economic actors in Sweden, and
- Add emissions by aviation, navigation and land transport from Swedish economic actors abroad
As an approximation, the environmental accounts residence adjustment currently includes emissions from international bunkers, that is, international aviation and navigation arriving and refuelling at Swedish airports and harbours. A simplified assumption is thus made that emissions resulting from foreign land transports in Sweden are equal to emissions resulting from Swedish land transports abroad and that emissions related to what Swedish ships and planes bunker abroad are equal to emissions related to what foreign ships and planes bunker in Sweden.
Indirect emissions resulting from imports and other consumption of goods and services are not included. Emissions and removals resulting from land use and land use change (LULUCF) and carbon capture and storage (CCS) are not included.
Annual Environmental Accounts on emissions to air by industry currently has a production time of 15 months. There is a demand for more up-to-date statistics on emissions to air of greenhouse gases. To meet this need, Environmental Accounts at Statistics Sweden has developed quarterly statistics on emissions to air by industry, which are also used to produce preliminary annual statistics. These quarterly statistics are also used to produce preliminary data for T-1, and this data is delivered to Eurostat.
Quarterly statistics on all greenhouse gases and a number of air pollutants are available in Sweden’s Statistical Database. Excel spreadsheets are also available for download on Statistics Sweden’s website, and include data and figures on greenhouse gas emissions and emissions intensities by value added and per employee.
The SEEA analytical web tool contains the collected statistics about this area – from production to demand – including statistics on environmental economic steering instruments, economic development and environmental pressure from production and final demand.
Next publishing will be
The next statistical news, on quarterly emissions to air for the third quarter 2018, is scheduled for publication in January 2019.
Statistical Database
More information is available in the Statistical Database
Feel free to use the facts from this statistical news but remember to state Source: Statistics Sweden.
