Income and taxes 2022
Lower economic standard
Statistical news from Statistics Sweden 2024-01-23 8.00
For the first time since the 1990s, the economic standard fell in 2022. The reason is inflation, which was higher than the increase in income.
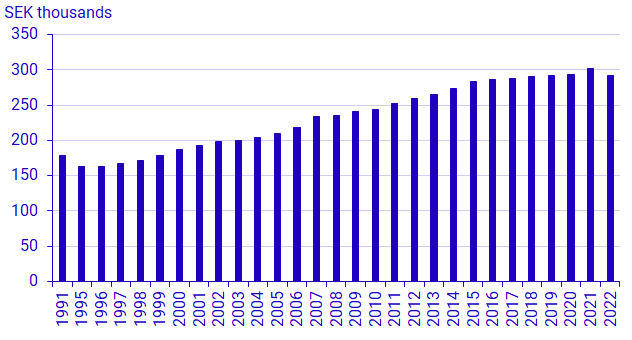
The median value of the household's economic standard increased by 5 percent between 2021 and 2022 in current prices. But because inflation was even higher – 8.4 percent in annual average – incomes fell in real terms when previous years' income amounts are converted to 2022 price levels. In fixed prices, the median value decreased by 3.2 percent. A reduction in the economic standard has not occurred since the economic crisis of the mid-1990s.
Split picture of income inequality
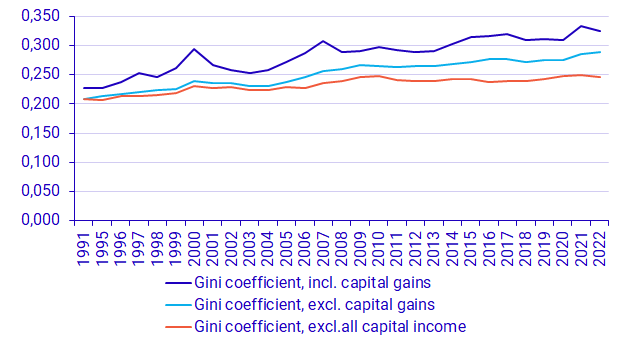
The change in income inequality in 2022 diverge depending on which income type is studied. The Gini coefficient, an overall measure of income inequality, decreased for the economic standard including capital gains, implying a more even distribution. The reason is that capital gains decreased in 2022 compared to the year before. In contrast, the Gini coefficient continued to increase for income excluding capital gains, but including other capital income such as dividends and interest. This means that income inequality, for that income type, were the highest since these statistics started. The increase is largely due to a continued increase in dividends.
Definitions and explanations
Economic standard: For a comparison of disposable income between different types of households, disposable income of the household is placed in relation to the number of adults and children in the household.
Disposable income is the sum of all taxable and non-taxable income less taxes and other negative transfers (such as repaid study loans) of all household members.
Gini coefficient: The Gini coefficient is used to show inequality in the income distribution. The coefficient is a value between 0 and 1. A high coefficient value indicates greater inequality than a low value.
Capital income and capital gains: Capital income is the sum of interest, dividends, imputed income for investment savings account (ISK) and investment funds and capital gains minus capital losses. Capital gains arises from the sale of housing, securities etc.
Fixed prices: The income and economic standard presented in this statistical news have been calculated at fixed prices to the 2022 price level using the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
Statistical Database
More information is available in the Statistical Database
Feel free to use the facts from this statistical news but remember to state Source: Statistics Sweden.
