Research and development (R&D) in Sweden:
Swedish businesses increased R&D expenditure in 2015
Statistical news from Statistics Sweden 2016-09-08 9.30
According to preliminary information, both the business sector and the higher education sector increased their intramural (in-house) R&D expenditures in 2015 compared with 2013. The business sector spent SEK 95 billion in total while R&D expenditure in the higher education sector amounted to SEK 37 billion. R&D in the government sector amounted to SEK 5 billion, which is a decrease compared with 2013.
The results are based on preliminary figures from Statistic Sweden’s R&D surveys. The numbers are therefore not definite and may be revised. All monetary figures are presented in constant prices of 2015.
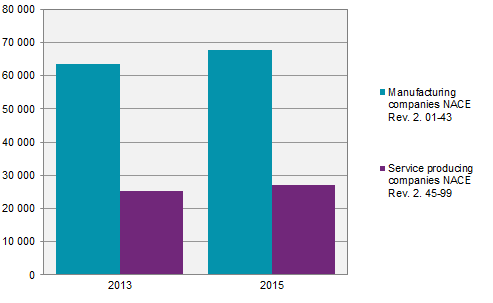
Both intramural expenditures and the number of full-time equivalents (FTEs) increased compared with 2013. The intramural expenditures amounted to SEK 95 billion, an SEK 6 billion increase compared with 2013. Manufacturing companies spent SEK 68 billion while service producing companies’ intramural R&D expenditure was SEK 27 billion. The number of FTEs increased from roughly 56 000 to almost 59 000. The increase was higher among men than among women. However, the share of FTEs among men and women remained the same as in 2013.
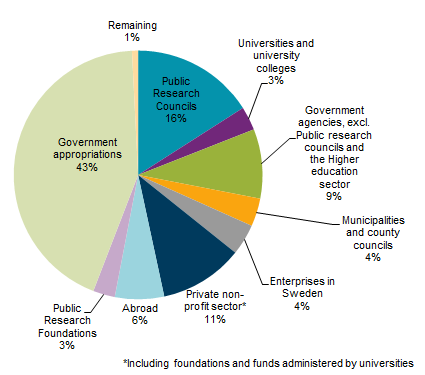
Intramural R&D expenditure in the higher education sector corresponded to SEK 37 billion in 2015, which is nearly an increase of SEK 2 billion from 2013. Government appropriations (including ALF resources) are the main source of funds of the R&D revenues. Funding from the Swedish Research Council and private non-profit organisations are the main sources of the increase. The number of FTEs in the higher education sector increased marginally since 2013 and amounted to almost 20 000 in 2015.
Expenditures for intramural R&D in the government sector amounted to almost SEK 5 billion in 2015, almost an 80 million decrease from 2013. The government agencies sub-sector was the only sub-sector that increased intramural R&D expenditures. Despite the decrease in expenditures, the FTEs in the government sector equalled 4 000, which is a 30 percent increase compared with 2013.The reason for the rise of FTEs was because more county councils were able to submit information regarding personnel regarding 2015.
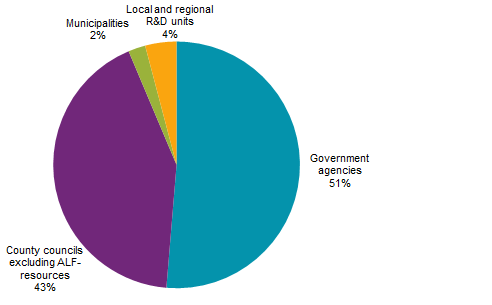
Note: The private non-profit sector is not included in the preliminary figures.
Definitions and explanations
Intramural R&D
Activities carried out in Sweden by the organisation's own personnel, or by consultants in an R&D project led by the organisation, where the organisation's personnel have worked together with the consultants. Intramural R&D includes R&D assigned by others.
R&D Expenditures
R&D expenditures include current expenditures and investments for intramural R&D. Current expenditures refer to labour costs, consultant fees, and other current expenditures. Investments include Buildings, land and real estate, Machinery and equipment, and Software.
Full-Time Equivalent
A person-year is the work that one full-time employee does in one year. A full-time employee that uses half of his or her time on R&D during a year has consequently performed 0.5 R&D person-years.
NACE
The R&D statistics within the business enterprise sector are presented according to the European activity classification NACE rev. 2 on 4-digit level. The enterprises are divided into manufacturing enterprises (NACE Rev. 2. 01-43) and Service producing enterprises (NACE Rev. 2. 45-99).
ALF-Resources
ALF (Agreement for Medical Training and Research) refers to an agreement about compensation that the central government pays to certain county councils to cover the majority of costs that clinical training and research incur.
Publication
More information about this survey is available in Swedish,
Research and development in Sweden - an overview, international comparisons etc (pdf).
Feel free to use the facts from this statistical news but remember to state Source: Statistics Sweden.
